In the last blog post I talked about the basic concepts of “Containers” and about Docker’s components that makes it easy to work with containers. Since Docker is a virtualization technology, to understand its benefits and drawbacks, we should be clear with how it differs from the currently most widely used virtualization technology “Virtual Machines”.
Virtual Machine
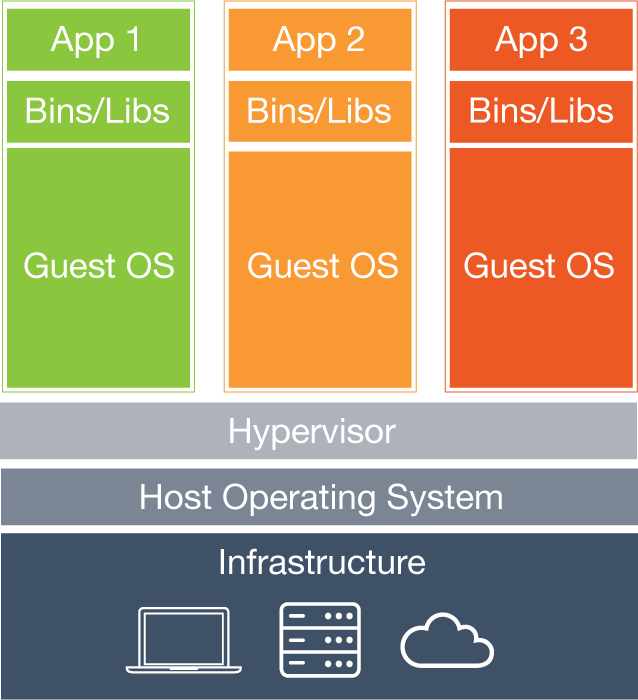
A virtual machine (VM) is an application environment that is installed on software which imitates dedicated hardware. For an end user Virtual Machines behaves just like they have dedicated hardware. This is achieved by a specialized software called hypervisor. A hypervisor emulates the CPU, memory, hard disk, network and other hardware resources completely, enabling users to have the same experience on virtual machines as they would have on dedicated hardware.
Hypervisors allow virtual machines to run different OS like ubuntu, windows, RedHat, CentOS etc. on the same physical machine.
Benefits of Virtual Machines
- Hardware-independence of system and applications
- Better Hardware Utilization
- Ease of Management
- Reduction in “Total Cost of Ownership”
- Can encapsulate OS + Application as units
- Reduce hardware vendor lock-in
- Faster server provisioning
- Easier backups
Docker Containers
Containers provide a lightweight and high-speed alternative to Virtual Machines. Containers run inside a host operating system and provide very convenient way of application process and network isolation. A virtual machine runs its own kernel and operating system, whereas container shares its kernel with the host operating system. Even though there can be multiple containers running on the host machine, each of these containers containers is completely isolated from one another.
Please ready my last bolg post to understand the concepts of containers.

Benefits of Docker Container
- Rapid application deployment
- Portability across machines
- Version control and component reuse
- Reduce OS overhead. Enable the use of small-footprint operating system.
- Spin up containers when workload is heavy. Retire them when they are no longer needed.
- Design applications as suites of services, each written in the best language for the task.
Benefits of Docker Containers over VM
A docker container starts in seconds and sometimes even less that a second, where as a virtual machine typically talkes around 15 minutes to start. Microservices is one of the most recent and widely adopted trends. Deploying hundreds of services independently in VMs seems like impractical, whereas by using light weight containers, its easier to adopt the microservices architecture. A virtual machine runs its own kernel and operating system, whereas container shares its kernel with the host operating system. When using containers there are a fewer operating systems to manage. A Docker image is made up of layers which enables tracking changes to environment. Developers can make incremental changes and easily commit, push and pull these changes to the repository. This makes it very easy for developers to colleborate and work as a team. Its makes it very easy for the different components of the application to use different versions of the same language or libraries. So in a single machine you can deploy applications that use different versions of Java, PHP etc.